🔍 Auto‑color ELF Malware Analysis Report
📄 Executive Summary
Auto‑color is a 64-bit ELF malware targeting Linux systems. First observed in April 2025, it uses LD_PRELOAD injection for persistence, drops auxiliary payloads under /var/log/cross/, and connects to a C2 domain check.linux-kernel.xyz. It performs privilege escalation, reads sensitive files, and modifies file permissions to maintain stealth and control.
IP: 18.167.12.195
Communication Port: 5353 (abused)
🧬 Malware Overview
- Name: Auto‑color (auto_color.elf)
- Type: Linux Backdoor / LD_PRELOAD Malware
- Platform: Ubuntu Linux (22.04.2 tested)
- Format: ELF 64‑bit, dynamically linked, stripped
- Size: ~216 KB
- First Seen: April 19, 2025
- Interpreter: /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2
⚙️ Infection & Execution Flow
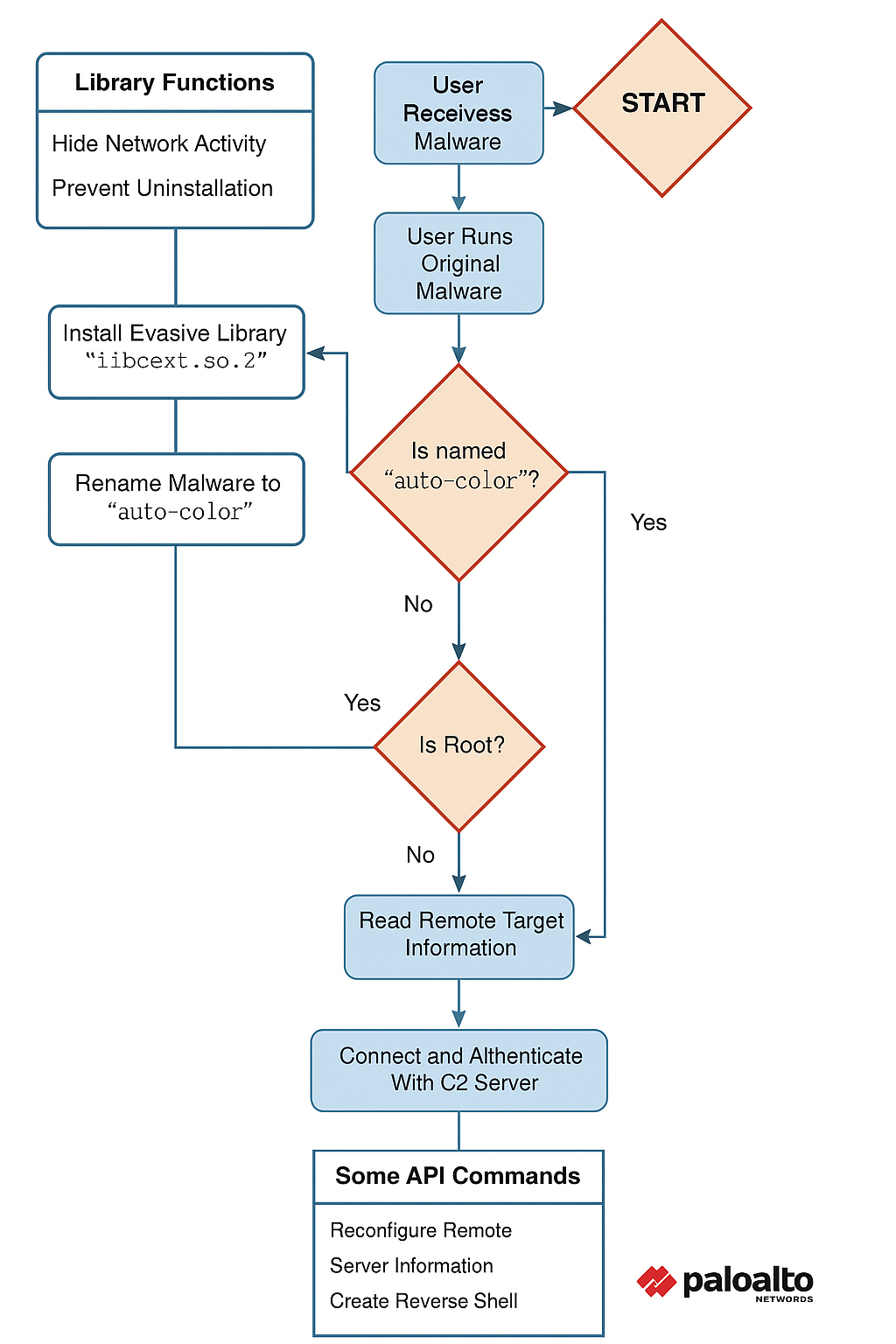
Initial Execution:
- Executed via sudo with root privileges
- Run from a parent shell using: chown + chmod +x + sudo -i ./auto_color.elf
Behavioral Flow:
- Reads passwd and other profile files
/etc/passwd - Creates directory and files under
/var/log/cross/ - Drops malicious shared object:
libcext.so.2 - Modifies ld.so.preload for persistence
/etc/ld.so.preload - Spawns shell processes: bash, dash, locale-check
📦 Static Analysis
- MIME: application/x-pie-executable
- Architecture: x86‑64 (Little Endian)
- Build ID: 08a8401aef311e569e8bcbc3b46829560334ec0a
- Stripped: Yes
- Linked As: Shared object
Hashes:
MD5: a30f5c43b437c940a4d5e940d37106ca
SHA1: f91623fa3d8c69b0a3fc1ed2172290af492be37b
SHA256: e463921880458ee1de65cc3f77ae07a3b9a3ae151de8b6c52ea382c8d6146b0f
🧪 Dynamic Behavior
- Drops files in
/var/log/cross/ - Creates (malicious shared object)
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcext.so.2 - Edits for runtime injection
/etc/ld.so.preload - Spawns shell commands and reads sensitive files
🌐 Network Activity
- Domain: check.linux-kernel.xyz
- IP: 18.167.12.195 (Amazon AWS - HK)
- Port: 5353 (C2 over non-standard port)
- Other Traffic: connectivity-check.ubuntu.com, snapcraft, GNOME services
🛑 Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
File Paths:
/home/user/Desktop/auto_color.elf/var/log/cross/auto-color/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcext.so.2/etc/ld.so.preload
🎯 MITRE ATT&CK Techniques
- Initial Access: T1078 – Valid Accounts (sudo misuse)
- Execution: T1059 – Command & Scripting Interpreter
- Persistence: T1574.006 – LD_PRELOAD Hijacking
- Privilege Escalation: T1068 – Exploitation via sudo
- Defense Evasion: T1027 – Obfuscated Files (stripped ELF)
- Credential Access: T1003 – Reads /etc/passwd
- C2: T1071.001 – Application Layer Protocol
🔐 Mitigation & Recommendations
- Monitor below file for unauthorized changes
/etc/ld.so.preload - Block IP Below IP and Domain:
18.167.12.195check.linux-kernel.xyz - Inspect below port for abnormal outbound connections
5353 - Delete all the files located in below path
/var/log/cross/libcext.so.2 - Reimage systems if full cleanup is uncertain
🕵️♂️ Real-World Case: SAP NetWeaver Exploit
In April 2025, attackers exploited CVE-2025-31324 (SAP NetWeaver) to deliver Auto‑color malware to a U.S. chemicals company. This marked the first observed use of an SAP RCE flaw to deploy the ELF backdoor.
Attack Timeline:
- April 25: SAP scanning and exploitation began
- April 27: Payload download and DNS tunneling activity
- April 28: Auto‑color executed with root privileges
The malware suppressed its malicious activity if C2 was unreachable, appearing benign and evading detection. This shows an advanced level of evasion logic and adaptive behavior.
✅ Conclusion
Auto‑color is a stealthy Linux ELF malware using LD_PRELOAD hijacking, stripped binaries, and system path masquerading. Its capabilities make it highly resilient and difficult to detect. Organizations should strengthen file integrity monitoring, patch management, and network egress controls to mitigate such threats.